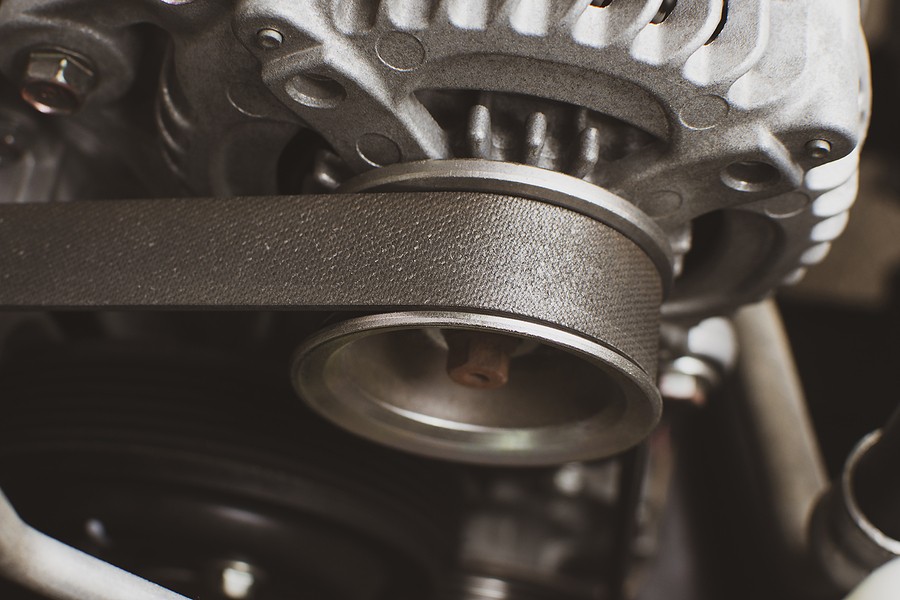
In the vibrant sphere of automotive mechanics, one component holds significant sway in ensuring a vehicle operates smoothly – the alternator. This key player in your vehicle's power system is integral in maintaining battery charge and powering electrical systems, acting as the unsung hero in your vehicle's powerhouse. Understanding the symptoms of a malfunctioning alternator can be a lifesaver, helping you avoid unforeseen breakdowns and hefty repair bills. In this extensive guide, we walk you through the signs that point towards a failing alternator, aiding you in keeping your vehicle in prime condition.

1. Introduction to Vehicle's Alternator
1.1 Definition and Functionality
An alternator, a cornerstone in modern vehicles, operates as an electric generator, setting in motion the moment your engine starts. Tasked with charging your car battery, it also powers the vehicle’s electrical system, ensuring smooth functioning. The alternator transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy through alternating current. This sophisticated yet rugged device keeps the power flowing, the battery charged, and the electrical systems running, making it indispensable in today’s automobiles.
1.2 History and Evolution
The alternator has come a long way from its inception. Initially, automobiles were equipped with a DC dynamo with inherent limitations in efficiency and power output. The advent of alternators, capable of generating alternating current, marked a significant upgrade, offering higher power output and better efficiency, fostering a revolution in the automotive industry. These powerhouses are more compact, lightweight, and capable of working under high-temperature conditions, ensuring the vehicle’s electrical systems remain powered at all times.
1.3 Importance in Modern Vehicles
Modern vehicles house an array of electrical components, each necessitating a steady power supply for optimal functioning. From fuel injection systems to advanced GPS units, the alternator supports them all, rendering it the backbone of modern automotive electrical systems. A malfunctioning alternator can cause a cascade of issues, impacting various subsystems and leading to compromised safety and performance. Therefore, being vigilant about the health of your alternator is not just a matter of maintenance but of safety as well.

1.4 Components and Structure
An alternator's core comprises several key components, including the rotor, stator, diode rectifier, voltage regulator, and bearing. The rotor and stator work harmoniously to generate electrical power, with the diode rectifier converting the AC output to DC. The voltage regulator maintains an optimum output voltage level, protecting the battery and other electrical components from voltage spikes. Understanding these components will provide insights into potential malfunctioning symptoms and the necessary steps for remediation.
2. The Importance of a Functioning Alternator
2.1 Battery Charging
The alternator is the powerhouse, consistently charging the battery while the vehicle runs. A healthy alternator ensures the battery is always at an optimal charge level, ready to start your car and power various electrical systems. When the alternator malfunctions, the battery's charge depletes rapidly, leaving you with a vehicle that refuses to start or electrical systems that falter unpredictably.
2.2 Powering Electrical Systems
Today’s vehicles are a marvel of electrical engineering, hosting many systems like the entertainment unit, GPS, air conditioning, and lighting, all relying heavily on the alternator for power. The alternator channels the necessary electricity to these units, facilitating a harmonious driving experience. A failing alternator can manifest as fluctuating power outputs, causing intermittent issues or complete failure of these systems.

2.3 Supporting Engine Performance
The alternator supports the engine in a more indirect yet critical manner. Many engine components require electrical power to function optimally. A malfunctioning alternator can lead to a sporadic power supply, causing the engine to run erratically or stall. Understanding how the alternator contributes to engine performance can help pinpoint issues before they escalate into major problems.
2.4 Prolonging Vehicle Lifespan
A properly functioning alternator can considerably extend the lifespan of your vehicle. Ensuring that the battery and other electrical components receive a steady, appropriate voltage prevents unnecessary wear and tear. Consequently, being aware of the symptoms of a failing alternator can prevent other problems, saving both time and money in the long run.
3. Recognizing Symptoms of a Malfunctioning Alternator
3.1 Warning Lights
Your vehicle's dashboard serves as a sentinel, keeping a vigilant eye on the various components' health, including the alternator. Modern cars often have a dedicated warning light that illuminates when the alternator is not functioning optimally. This warning light, usually shaped like a battery or depicted as “ALT” or “GEN,” is your first indication of potential trouble. If you notice this light flickering or staying lit, it's a sign to inspect your alternator promptly.

3.2 Dimming or Flickering Headlights
The alternator directly powers the headlights while the vehicle is running. If the alternator starts to fail, you may notice your headlights dimming or flickering, especially when you rev the engine or operate at high speeds. This clearly indicates a fluctuating power supply from the alternator, necessitating a thorough check-up to prevent further complications.
3.3 Weak or Dead Battery
A weak or dead battery is often a symptom of a malfunctioning alternator. If your battery seems to lose charge quickly or struggles to hold a charge, it might be because the alternator is not adequately recharging it. To differentiate between a battery issue and an alternator problem, you can recharge the battery fully and see if it drains rapidly, indicating an alternator issue.
3.4 Unusual Noises
Alternators contain various rotating parts, including bearings and belts. Over time, these components can wear out, leading to unusual noises emanating from the alternator. These noises can be squealing, growling, or grinding sounds, signaling that it’s time for an alternator inspection and possible replacement.

4. Diagnostic Tests for Alternator Issues
4.1 Visual Inspection
Before delving into advanced diagnostic tests, start with visually inspecting the alternator. Check for loose connections, worn belts, and any visible signs of damage. Sometimes, the issue can be as simple as a loose belt or corroded connection, which can be fixed easily, restoring the alternator's function.
4.2 Voltage Test
A voltage test can provide a quick insight into the alternator's performance. Using a voltmeter, you can check the voltage output at the battery terminals with the engine running. A healthy alternator should output between 13.6 and 14.6 volts. If the voltage is outside this range, it indicates an alternator issue.
4.3 Load Test
Load testing involves measuring the alternator's performance under various electrical loads. This test helps to ascertain the alternator's capacity to handle the electrical demands of your vehicle. Professional mechanics usually conduct this test using specialized equipment to accurately gauge the alternator's health.

4.4 Professional Diagnosis
Sometimes, diagnosing an alternator issue can be complex, requiring the expertise of a professional mechanic. If you cannot pinpoint the problem through visual inspections or voltage tests, consider consulting a professional to analyze the alternator's condition and appropriate remedies comprehensively.
The journey into understanding and diagnosing a malfunctioning alternator is extensive. In the upcoming sections, we will investigate preventative measures, repair options, and tips on selecting a quality replacement alternator.
5. Preventative Measures and Maintenance
In the vast world of automotive care, prevention is often better than cure. Here, we look at various strategies to help prevent alternator malfunction, potentially saving you from costly repairs and unexpected breakdowns.
5.1 Regular Inspections
A prudent strategy is incorporating regular alternator inspections into your vehicle maintenance routine. Regular check-ups can help identify early signs of wear and tear, facilitating timely interventions. These inspections typically involve checking the alternator belts for cracks and signs of aging and ensuring the connections are clean and secure.
5.2 Battery Maintenance
A well-maintained battery not only ensures a smooth start every time but also reduces unnecessary strain on the alternator. By keeping the battery in good condition, the alternator doesn't have to work as hard to keep it charged, prolonging its life.

5.3 Keeping Electrical Loads Within Limit
Every alternator has a maximum capacity of electrical load it can handle. To avoid overloading the alternator, keep the electrical loads within reasonable limits. Avoid using multiple high-power accessories simultaneously for extended periods, as this can lead to overheating and eventual failure of the alternator.
5.4 Prompt Repairs
Whenever you identify a potential issue with your alternator, attend to it promptly. Delaying repairs can escalate the problem, leading to more extensive damage and higher repair costs. A quick response often means a minor repair and a complete alternator replacement.
6. Repair and Replacement Options
At times, despite your best preventative efforts, the alternator may still falter. In such cases, it’s essential to understand the various repair and replacement options available.
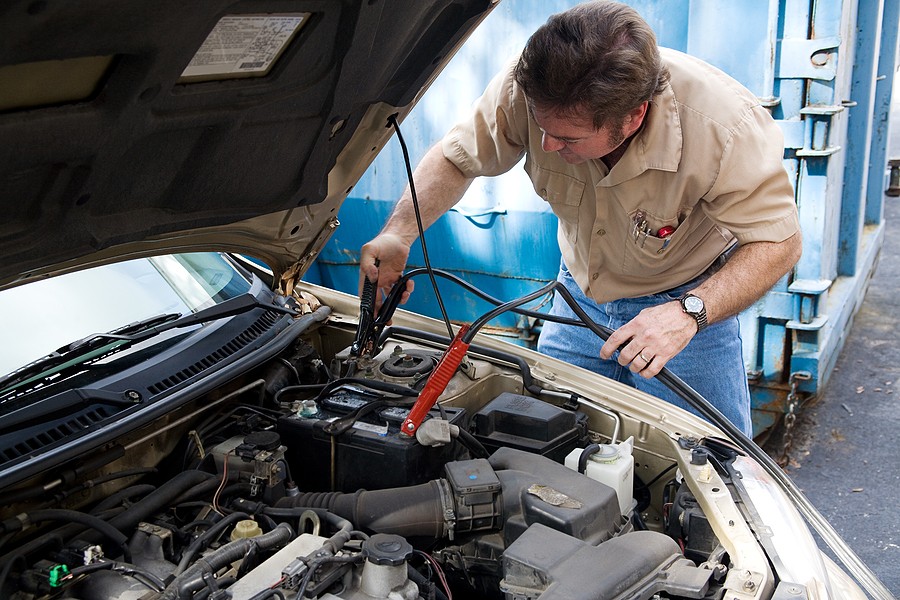

6.1 DIY Repairs
For DIY enthusiasts, minor alternator issues like a loose belt or a faulty connector can often be fixed at home with the right tools and some basic knowledge. Many online resources can guide you through the process, helping you restore your vehicle's electrical health without a trip to the mechanic.
6.2 Seeking Professional Help
When faced with more serious issues, it's advisable to seek professional help. Experienced mechanics have the tools and expertise to diagnose and fix alternator problems accurately, ensuring your vehicle's long-term reliability.
6.3 Choosing Quality Replacement Parts
Opting for quality replacement parts can be a wise investment when replacing a faulty alternator. While it might be tempting to go for cheaper options, quality parts will likely offer better performance and a longer lifespan, providing better value for money in the long run.
6.4 Understanding the Costs Involved
Understanding the potential costs of alternator repairs and replacements can help you make informed decisions. Costs can vary widely depending on your vehicle's make and model, the repair's complexity, and the parts chosen for replacement. A clear understanding of these aspects can prevent surprises when the bill arrives.

7. Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we answer some of the most common questions about alternator malfunctions, providing a comprehensive resource to address all your concerns.
7.1 Can a Car Run with a Faulty Alternator?
Yes, a car can technically run with a faulty alternator, but not for long. The battery will eventually drain, as it's not being recharged by the alternator, leading to a breakdown. Getting to a service station or mechanic as soon as possible is advisable if you suspect alternator issues.
7.2 How Long Does an Alternator Last?
An alternator can last between 7 and 11 years, or approximately 100,000 to 150,000 miles. However, this lifespan can vary based on the vehicle's make and model and how well it is maintained.
7.3 What Are the Steps to Replace an Alternator?
Replacing an alternator involves several steps, including disconnecting the battery, removing the serpentine belt, unplugging the electrical connections from the alternator, removing the bolts holding the alternator in place, and installing the new alternator in reverse order.
7.4 How to Differentiate Between a Battery and Alternator Issue?
Distinguishing between a battery and alternator issue can sometimes be tricky. A simple way is to charge the battery and start the vehicle fully. If the battery drains rapidly or the vehicle has difficulty starting, it could indicate an alternator issue. Another method is to measure the voltage at the battery terminals with the engine running, as discussed in the diagnostic tests section.
8. Conclusion: Key Takeaways and Final Thoughts
In this comprehensive guide, we have journeyed through the vital landscape of understanding the symptoms of a malfunctioning alternator, preventive measures, and the necessary steps to undertake if faced with an alternator issue. Recognizing the signs early can prevent further complications, ensuring your vehicle remains reliable and serves you well for many years.
8.1 Early Detection is Key
Spotting the symptoms of a failing alternator early on is crucial. It not only saves you from potential breakdowns but also protects other vehicle components from damage, prolonging the overall life of your vehicle.
8.2 Invest in Quality
Investing in quality replacement parts and professional services can make a significant difference in the longevity and performance of your vehicle. A well-maintained alternator can offer you peace of mind, knowing that your vehicle's electrical system is in capable hands.

8.3 Stay Educated
Educating yourself about the various aspects of vehicle maintenance, including understanding the alternator's functioning, can empower you to make informed decisions regarding repairs and replacements, ensuring a smoother, safer driving experience.
8.4 Final Thoughts
As we conclude this journey, we hope this guide serves as a comprehensive resource, assisting you in navigating the complexities of alternator malfunctions with ease and confidence. Happy driving!



